General tips
Save filters
Users can save their configured filters by clicking Copy link. This link can then be shared with others or used in Dashboard buttons.

Filter by date parameter
It is common to want to filter data by date, for example, by having this type of parameter in dashboards:
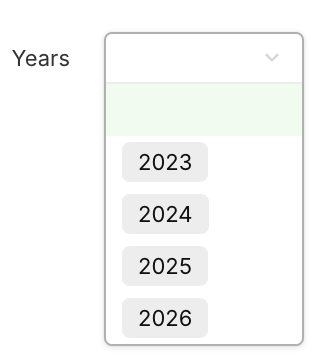
This parameter can then be used for example for the count of instances for the Concept A, such as counting instances created within a specific year: for 2024, only the instances created in 2024 needs to be taken into account, etc.
In order to do it, the following steps can be followed:
Create a concept Years:
Create a date field, with the correct granularity. (the name of the field will be Date Year to continue the example).
Use only this field for the concept chip representation.
Create the needed instances.
Create a multidim (Concept A x Years) boolean field. The name of the field will be Is created this year ? to continue the example.
Have for Input1: Concept A > Dimension > Created At and for Input2: Years > Dimension > Date Year.
The formula can then be:
IF(OR(COUNT(Input2)=0, YEAR(Input2)=YEAR(Input1)), TRUE, FALSE)(By having the condition COUNT(Input2)=0, if the dimension Years is empty, then the formula will return TRUE. This is useful for example in the Dashboard when no instance is selected for the parameter Years, for taking into account all the instances, regardless the Created At date).
Use the multidim field to filter the instances.
In the formula counting the number of instances of Concept A, add the dimension Years.
In the filter of Input: Concept A > All instances, create a filter that use the field Is created this year ? with the proper mappings:

Add a new parameter Years in the Dashboard:
Use the concept Years for that parameter.
Use the parameter Years for mappings in Dashboard widgets.
By following these steps, data can be filtered by date via a parameter in a dashboard.
Compare text, date, number, External Key etc with a path
In advanced filtering (via Turn into advanced condition), certain field types, such as text, date, and number, do not support direct comparison with values originating from a path. Only fixed (literal) values can be selected as comparison targets.
To enable comparisons between a field and a value coming from another concept through a path, an intermediate computed field must be created.
Use Case Example
Objective: retrieve all Data Domains that share the same External Key as a Use Case.
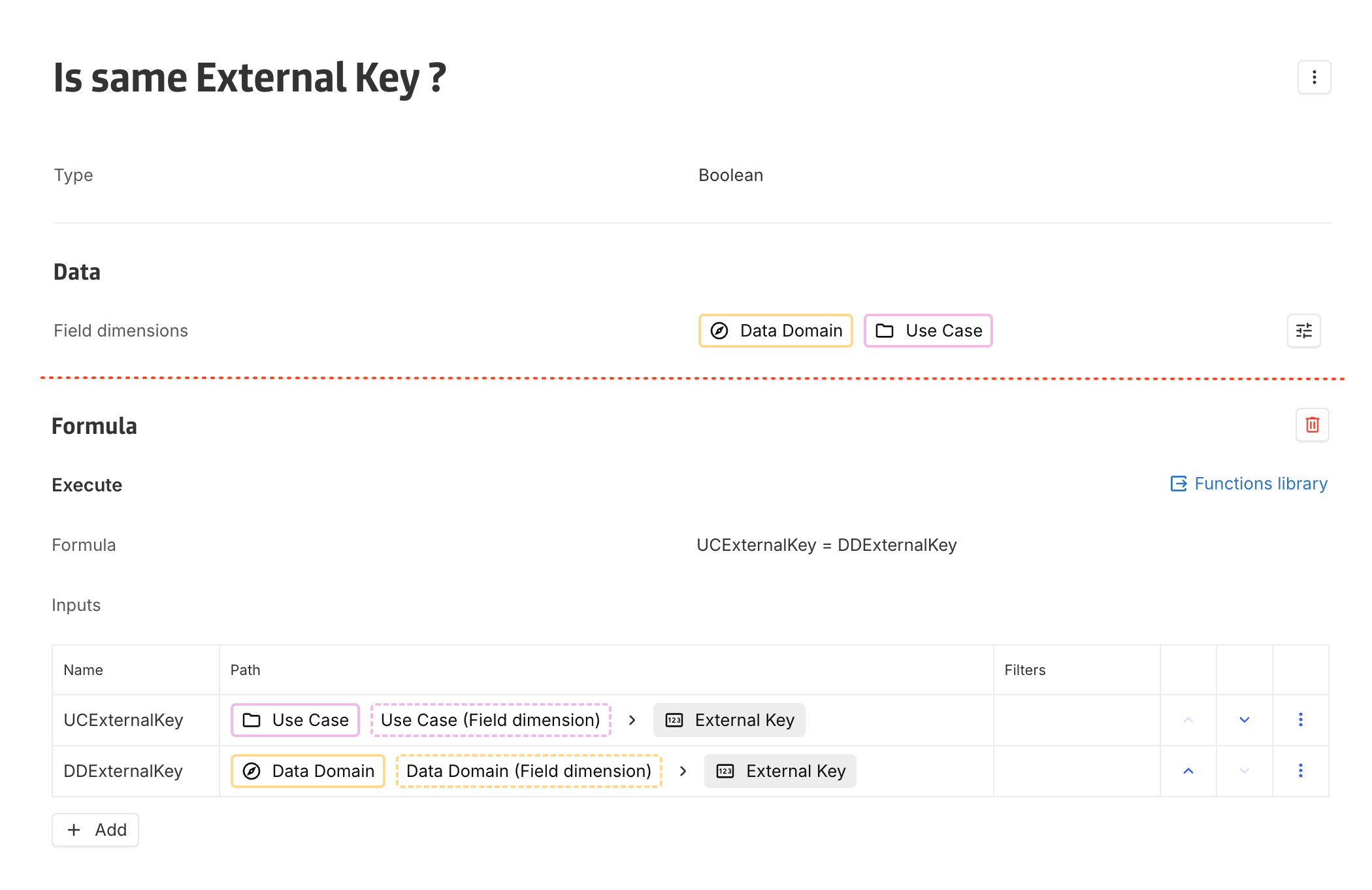
Step 1 : Create an Intermediate computed boolean field
A computed multidimensional boolean field must be created between the concepts Use Case and Data Domain.
This field should implement a formula that evaluates whether the External Key of the Data Domain matches the External Key of the Use Case.
Step 2 : Use a computed n-n association
Create a computed many-to-many association that returns all Data Domains whose External Key equals the External Key from the related Use Case.
The previously created computed boolean field is used as a filtering condition.
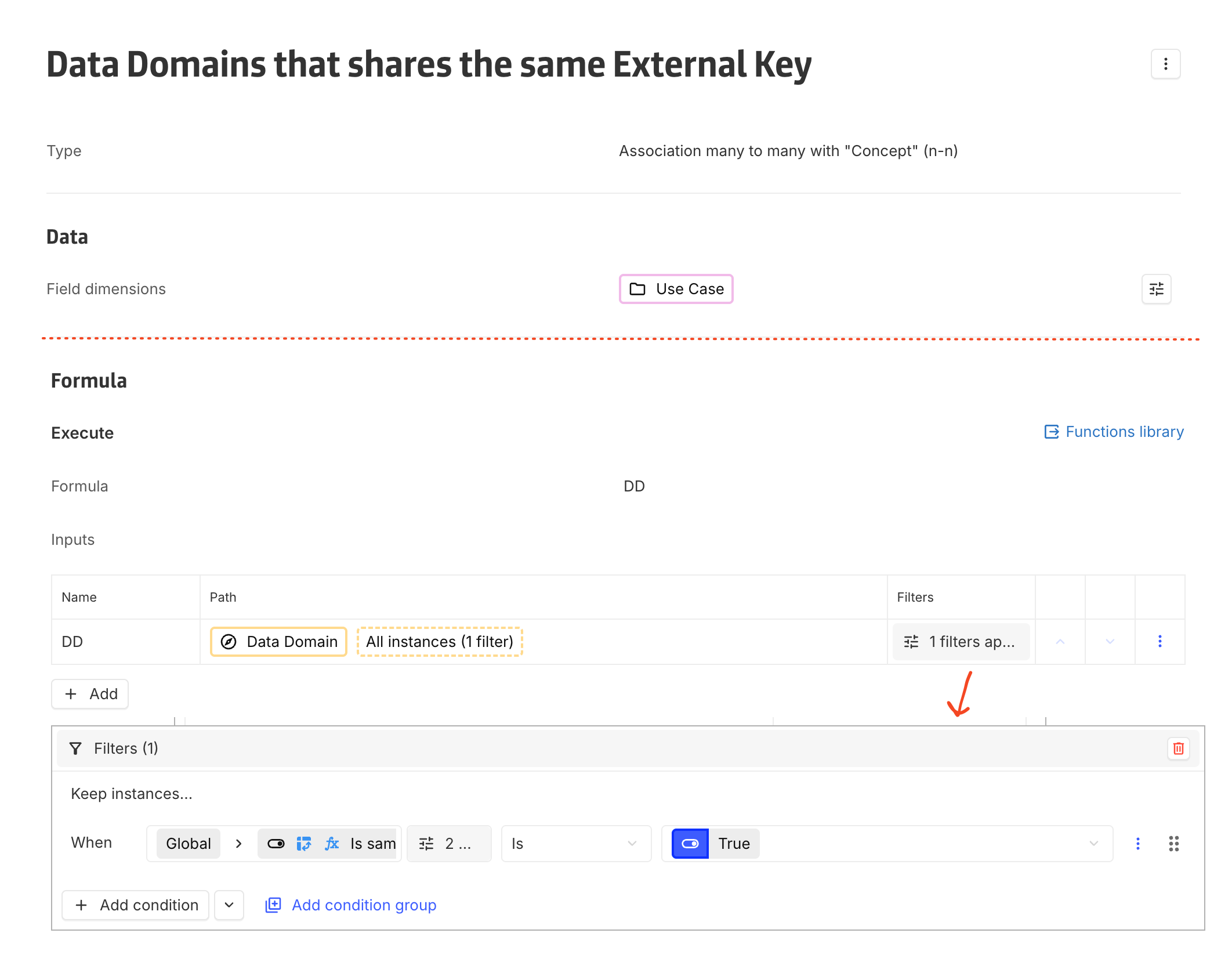
This approach enables comparison of dynamic values sourced from a path, even though advanced filters do not support such comparisons directly.
